
Have you heard about digital twins before? The idea first came up in the 1960s to create an Apollo living model to evaluate its failure by using a physical vehicle model with digital components. It is understandable that the concept has grown, but its core remains unchanged. A digital twin, in essence, is a model created specifically to reflect an object accurately. IBM also defines a “digital twin” as “a virtual representation of an object or system that spans its lifecycle, is updated from real-time data, and uses simulation, machine learning and reasoning to help decision-making.” Although digital twins are often mistaken for modeling, they go far beyond that. In digital twins, algorithms and mathematical operations are used to help users predict the behavior or 3D printed parts.
They are used in many different applications, from interior design to manufacturing. In addition, they are being used more and more in additive manufacturing. Markets and Markets estimated that the market for digital twins would be worth $6.9 billion in 2022. By 2027, it was expected to grow to $73.5 billion. Why would you want to use digital twins for 3D printing? What are the things you should know before doing this? We took a closer look.
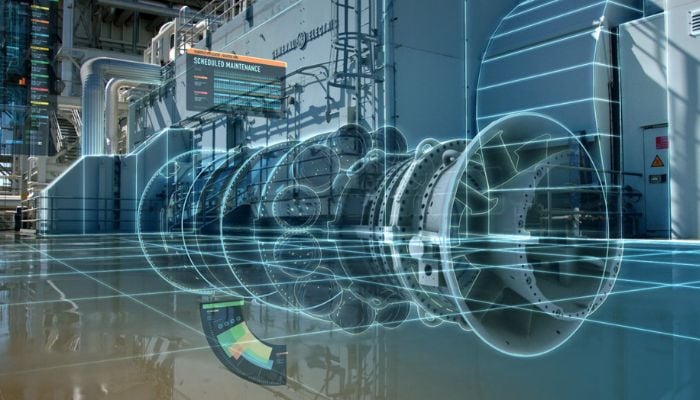
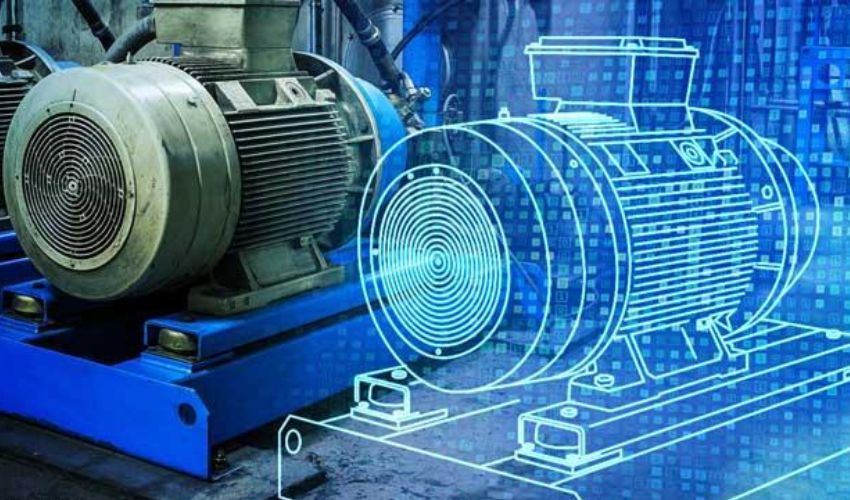
Digital twins are becoming more common in Industry 4.0. (Photo credit: GE).
Digital Twins for 3D Printing
Both additive manufacturing and digital twins are considered to be key components of Industry 4.0. The two have only recently been combined. It’s important to remember that many studies have concluded that 3D printing is well suited for digital twins. Why? By its very nature additive manufacturing is digital. Automation and AI has already found a place in AM because of this. From online design, to software for slicing, to programs that monitor the entire printing process. Digital twins are just another tool.
How can you use them then? Well, let’s first consider the process of integrating digital twins in 3D printing. As we have already said, a digital model is the starting point for a digital counterpart. This can be achieved through CAD and generative software. A 3D scanner is also increasingly being used, as it creates an exact model of the item in question. On the market, you can find a range of software designed to assist with 3D printers and digital twins. Consider those offered by Siemens, Simio, or Netfabb. This facilitates integration and thus promotes AM usage. It is also easy to imagine how it can be used in applications like reverse engineering spare parts, thanks to its ability of truly recreating products.
There are also a number of different forms in which digital twins may be created, so this must also be taken into consideration. One report suggests that digital twins for additive manufacturing can be divided up into four categories: process digital twins, equipment digital twins, facility digital twins and product digital Twins. Named after different aspects of the manufacturing process, digital twins are used to target specific areas. The digital twins of processes can be used for design, maintenance and production to reproduce a digital version 3D printing. Similar to equipment digital twins, they can be used to replicate printers. This provides important information for maintenance. Facility digital twins are similar to the first two types, but they take the entire floor of the factory into consideration. The last but not the least and the topic we will focus on in this guide are product digital twins. These are representations that allow a product or part to be tested, designed, and analyzed for performance prediction.

The digital twins are represented with 3D printed models (photo credit: Zhang, Li and Wei Zhou).
Why integrate digital twins into AM?
The combination of 3D printing and digital twins has a number of advantages. Particularly when it comes down to the quality control of components. Quality control is still a major concern, even though AM has evolved from its roots as rapid prototyping. With more and more parts being used in end-use applications, AM’s evolution has been dramatic. AM is a complex process that requires testing in order to avoid print failures. But this is in direct contrast to two of AM’s biggest advantages, namely cost and material production.
This can be overcome thanks to the use of digital models. Digital twins enable users to assess parameters directly thanks to the continuous stream of feedback. This allows the optimization of parameters without needing to test them physically. Digital twins allow for real-time monitoring of the 3D print process, resulting in even higher accuracy. In terms of AM quality control, this makes it more reliable. It is important to note that this could be a factor in increasing consistency, especially for industrial processes such as laser powder bed processes.
You can also find out more about the following:Digital twins can be used to model entire factories, not just single components. They can even be created for an entire floor of a factory. Additive manufacturing would become more industrialized if 3D printing farms were optimized for production on a whole floor, not just at the individual level.
It is not to suggest that there are no challenges. It is difficult to define and develop a digital twin, in part because the framework is not understood well. Digital twins and 3D printers will overcome this obstacle faster if they are used in conjunction. It is happening at a much larger scale already, thanks to the increasing use of AI tools and sophisticated machine learning. It will be fascinating to see the way digital twins and 3-D printing will be used in the future.
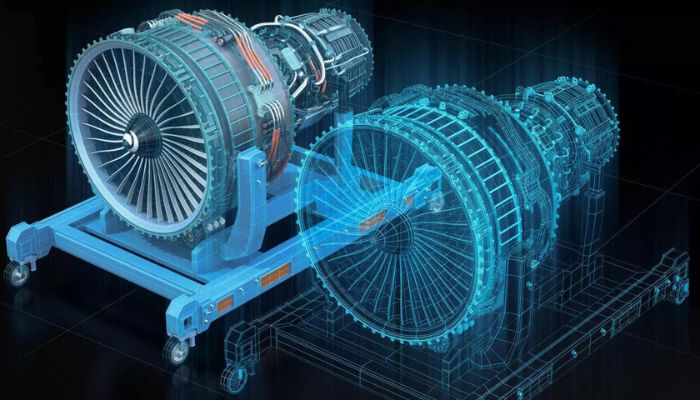
The use of digital twins for 3D printing is likely to increase, particularly in parts such as turbines (photo credit: Konica Minolta).
What do you think of the use digital twins for 3D printing? Please let us know by leaving a comment on this page or our The following are some of the most recent LinkedIn posts:, Facebook. Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Subscribe to our NewsletterYou will receive the latest news about 3D printing in your email! All our videos are available on our YouTube channel.
*Cover Photo Credits: Norlà Corporation